Overview
STROKE
In recent years stroke has become more common among people below the age of 60. The elderly, working-age adults and even teenagers can be threatened by stroke depending on a range of factors.
80% of strokes are Ischemic strokes |
|
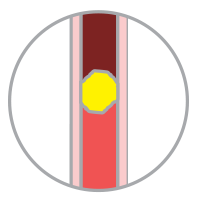 |
Embolic StrokeOccurs when a blood clot forms elsewhere (e.g. the heart), travels via the bloodstream, and clogs the tiny blood vessel in the brain. |
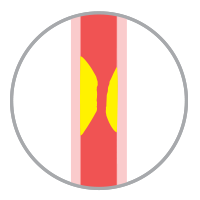 |
Thrombotic strokeRisk factors are advanced age, hypertension, diabetes, hyperlipidemia (high blood lipids including cholesterol, triglycerides and LDL), smoking, alcohol consumption and vascular diseases. |
20% of strokes are Hemorrhagic stroke |
|
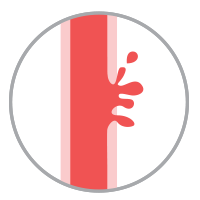 |
Hemorrhagic StrokeOccurs when weakened blood vessels rupture and bleed in the brain. The blood accumulates and puts pressure on the surrounding brain tissues, causing damages. |
Time is the key to stroke treatments. If any of the FAST symptoms appear, patients need to be in the care of stroke specialists as soon as possible. If reached in a timely manner, modern technology can greatly improve the chances of survival and complete recovery.
“1 million brain cells die every minute after stroke”

B.E.F.A.S.T.
If any of these symptoms occur, go to the hospital immediately.
- B – BALANCE : Loss of balance or or unsteadiness, sudden dizziness or a loss of coordination
- E – EYES : A sudden blurred or blackened vision
- F – Face Drooping : Uneven or lopsided smile. Especially with severe headache.
- A – Arm Weakness : Cannot raise the arms. Numb limbs. Unsteady walk.
- S – Speech Difficulty : Unable to speak or complete a sentence.
- T – Time
To call 1724, +662 226 4565
Call for an ambulance. The sooner the better.
BDMS Alarm Center: Stroke emergency service 24 hours
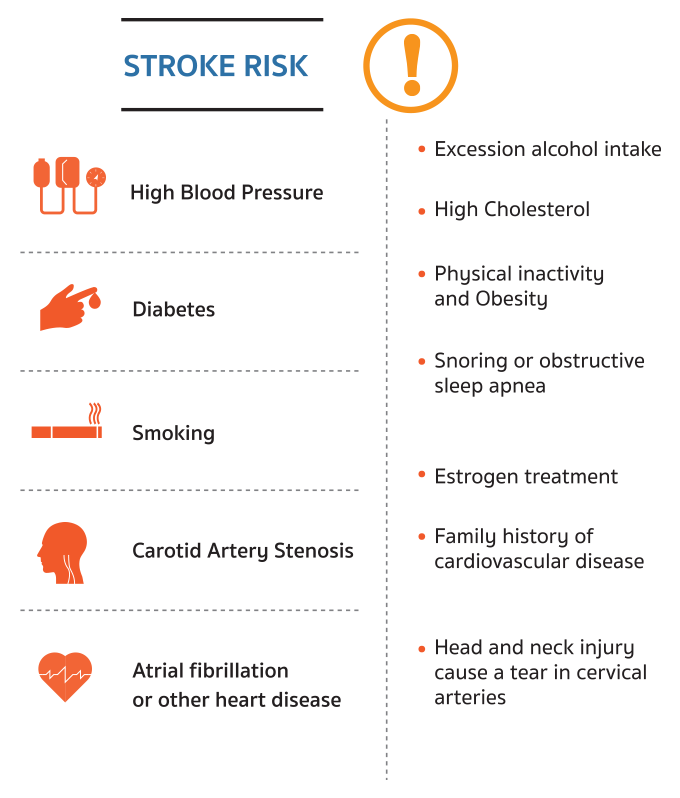
STROKE RISK
- Time to hospital: within 4 ½ hours after symptoms
If the stroke involves clotting in small blood vessels without any bleeding, the patient will be given intravenous r-TPA to dissolve the clot and restore blood flow to the oxygen deprived brain.
- Time to hospital: within 4 ½ – 24 hours after symptoms

Mechanical thrombectomy with stent retrievers for large-vessel clots. A catheter will be threaded through an artery to remove large blood clots without the need for open brain surgery.
Source : American Heart Association / American Stroke Association, Published Jan, 24,2018

