Parkinson’s disease develops from degeneration of the brain and nervous system that comes with old age. It is the second most common neurological disorder in elderly patients, caused by deterioration of the brain. Most common symptoms include shaking, muscle stiffness, slow movement, and loss of balance.
What is Parkin’s Disease?
Parkinson disease (PD) is a degenerative condition of the brain which is usually found in patients over 60 years of age. Only a few cases are found among younger people because of heredity. The truth is it is not difficult to find the root cause and treat. Nowadays, PD can be diagnosed by CI, MRI and PET scan. F – DOPA PET brain scan particularly targets the detection of abnormal dopamine production, since PD is caused by low level production of dopamine by the brain cells. This leads to tremors in the hands, arms, legs, jaws, and face. Careful examination will help doctors plan on the right course of action.

Aside from tremors, slow movement, impaired balance, difficult to swollow and speech, ability to speak in low, scruffy voice, other indications of PD include: constipation, dysuria and continence, erectile dysfuction, red eyes, and low blood pressure (BP). In some cases, the BP can drop when the patients just stand up, causing them to faint. They will need thorough examination.
How is PD Developed?
During the first stage, it may start in just one side of the body and causes tremors and difficulty in movement. Then, it will develop on both sides which may take 6 months to a year, after which patients will have impaired balance and will need a wheelchair. Eventually, they will be helpless and bedridden. These are the different stages of PD’s development.
How to Treat PD
Treatments can be both prescribed medication and surgery. Although few classes of medication are available, some patients may develop resistance to treatment. Some may be on medication for 4 – 5 years and the effects of medication may last longer than normal. Alternatively, some may not predict when it will go into effect. Most of these problems can be resolved when experienced doctors adjust the medication or recommend patients to avoid taking the medication with high protein content to avoid protein-drug binding. In patients who have became hypersensitive to medication, such as develop stiffness instead of tremors after awhile or develop side effects, surgery may be an option, albeit some limitations. Patients who have both Alzheimer’s disease and PD may not be eligible since they may develop depression and hallucination and surgery may not yield the best results.
New Technology to Treat PD
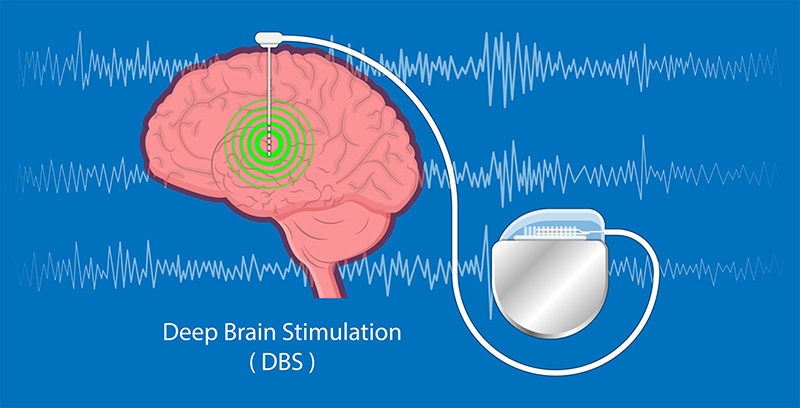
Today, there is a treatment called “Deep Brain Stimulation or DBS Therapy” in which electrodes are implanted into the deep part of the brain. The procedure is approved by the USFDA to help relieve over 100,000 patients around the world. There have been many cases in Thailand over the past 10 years, which helps reduce medication, control movement and improve the conditions in many patients, so they can return to their daily routine.
Moreover, there’s Medtronic DBS Therapy which requires implantation of a device in the brain as a substitute for medication to reduce tremor and other side effects that affect patients’ daily routine and mininize the risk of accicent with satisfactory result. The electrodes that are implanted in the brain is connected to a Pulse Generator which can be programmed remotely. The doctor will place a pacemaker-like into the patients’ body to send light electrical signals to an area in the brain that controls movement and to prevent some signals from the brain to cause impaired balance. The patients will be able to control their balance better and return to their daily routine happily.
During the past 10 years, aside from prescribed medicines, Thai physicians started to treat patients with electrode implantation. Batteries are then used to stimulate the brain at high frequency. This technique has become a standard in other countries since it has been proven to improve PD and other brain-related disorders, such as epilepsy, Alzheimer’s disease, as well as psychological conditions such as obsessive-compulsive disorder, depression, cervical tic, and muscle dystonia. After treatment with DBS, patients can be confident that the risk is low and complications are minimal.